The Constitution of the United States
The Bill of Rights & All Amendments
A highly accessible, easy to use online version full text transcript including the Bill of Rights and the rest of the Amendments with both sequential and subject indexes.
National Constitution Center
In the Interactive Constitution, scholars from across the legal and philosophical spectrum interact with each other to explore the meaning of each provision of the Constitution.
Here’s how the Interactive process works:
- Scholars are selected with guidance from leaders of the American Constitution Society and the Federalist Society—two prominent constitutional law organizations that represent different viewpoints on the Constitution.
- Leaders of each organization recommend scholars to write about each provision of the Constitution.
- The pairs of scholars find common ground, writing a joint statement of what they agree upon about that provision’s history and meaning.
- Then the scholars write individual statements describing their divergent views on that part of the Constitution.
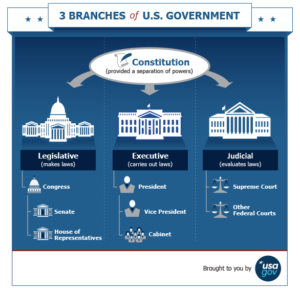
Branches of Government
Learn more about the executive, legislative, and judicial branches of the U.S. government.
What is the Electoral College?
The Electoral College is a process, not a place. The founding fathers established it in the Constitution as a compromise between election of the President by a vote in Congress and election of the President by a popular vote of qualified citizens.
County, State and Federal Government
One of the most complex forms of separation of power is the separate jurisdictions of City, County, State and Federal government.
In Hawaii, we have County Government
State government
and Federal (US) government
How to Become a U.S. Citizen
Learn how to become a citizen of the United States. Citizenship identifies an individual’s national origin. It defines his/her rights and responsibilities to that country (nationality). Most people have only one country of citizenship, but some can have dual nationality. U.S. citizens can be native-born, foreign-born, or naturalized. They owe their allegiance to the United States and are entitled to its protection.